Traps to Developers
A summarization of some traps to developers. There traps are unintuitive things that are easily misunderstood and cause bugs.
This article is mainly summarization. The main purpose is "know this trap exists". This article focuses on technical traps.
Summarization of traps
HTML and CSS
-
min-widthisautoby default. Inside flexbox or grid,min-width: autooften makes min width determined by content. It overrides effects offlex-shrink,width: 0andmax-width: 100%, etc. It's recommended to setmin-width: 0. Same formin-height. See also -
Horizontal and vertical are different in CSS:
- Normally
width: autotries fill available space in parent. Butheight: autonormally tries to just expand to fit content. - For inline elements, inline-block elements and float elements,
width: autodoes not try to expand. margin: 0 autocenters horizontally. Butmargin: auto 0normally becomemargin: 0 0which does not center vertically. But in a flexbox withflex-direction: column,margin: auto 0can center vertically. 1- Percentage
margin-topmargin-bottompadding-toppadding-bottomuse parent width as base value, not height. - Margin collapse happens vertically but not horizontally.
- Some of the above behave differently when layout axis flips (e.g.
writing-mode: vertical-rl). See also
- Normally
-
Margin collapse.
- Two vertically touching siblings can overlap vertial margin. Child vertical margin can "leak" outside of parent.
- Margin collapse doesn't happen when
borderorpaddingspcified. Don't try to debug margin collapse by coloring border. Debug it using browser's devtools. - Margin collapse can be avoided by block formatting context (BFC).
display: flow-rootcreates a BFC. (There are other ways to create BFC, likeoverflow: hidden,overflow: auto,overflow: scroll,display:table, but with side effects) - Related: margin can be negative. Negative margin can make elements overlap and make child leak outside of parent. BFC doesn't prevent this feature of negative margin.
-
If a parent only contains floating children, the parent's height will collapse to 0, and the floating children will leak. Can be fixed by BFC.
-
If the parent's
displayisflexorgrid, then the child'sfloathas no effect -
In these cases, it will start a new stacking context:
- The attributes that give special rendering effects (
transform,filter,perspective,mask,opacityetc.), andwill-changeof them position: fixedorposition: sticky- Specifies
z-indexandpositionisabsoluteorrelative - Specifies
z-indexand the element is inside flexbox or grid isolation: isolate- ...
Stacking context can cause these behaviors: 2
z-indexdoesn't work across stacking contexts. It only works within a stacking context.- Stacking context can affect the coordinate of
position: absoluteorfixed. (The underlying logic is complex, see also) position: stickydoesn't work across stacking contexts.overflow: visiblewill still be clipped by stacking context.background-attachment: fixedwill position based on stacking context.opacityis "relative" to parent. Childopacity:1in transparent parent won't make it more opaque than parent.
- The attributes that give special rendering effects (
-
On mobile browsers, the top address bar and bottom navigation bar can go out of screen when scrolling down.
100vhcorrespond to the height when the two bars gets out of screen, which is larger than the height when the two bars are on screen. The modern solution is100dvh. -
About scrollbar:
- In Windows, scrollbar takes space. But in macOS or mobile it doesn't take space 3.
- The space occupied by vertical scrollbar is included in width. Scrollbar "steals" space from inner contents. 4
- A top-level element with
width: 100vwoverflows horizontally if viewport has scrollbar that takes space.width: 100%can workaround that issue. - About scrollbar styling: the standard scroll bar styling supports color and width but doesn't support many other features (e.g. round corner scrollbar). The
-webkit-scrollbarnon-standard pseudo-elements supports these features but FireFox doesn't support them. In modern browser, if standard scrollbar styling is used, then the-webkit-scrollbarhas no effect.
-
position: absoluteis not based on its parent. It's based on its nearest positioned ancestor (the nearest ancestor that haspositionberelative,absoluteor creates stacking context). -
position: stickydoesn't work if parent (or indirect parent) hasoverflow: hidden. -
If the parent's width/height is not pre-determined, then percent width/height (e.g.
width: 50%,height: 100%) doesn't work. 5 -
CSS transition doesn't work between
height: 0andheight: auto. Solutions: -
In JS, reading size-related value (e.g.
offsetHeight) cause browser to re-compute layout which may hurt performance. It can also affect transition animation 8. -
display: inlineignoreswidthheightandmargin-topmargin-bottom -
Whitespace collapse. See also
- By default, newlines in html are treated as spaces. Multiple spaces together collapse into one.
<pre>doesn't collapse whitespace. But HTML parser removes a line break in the beginning and end of<pre>content.- Often the spaces in the beginning and end of content are ignored, but this doesn't happen in
<a>. - Any space or line break between two
display: inline-blockelements will be rendered as spacing. This doesn't happen in flexbox or grid.
-
text-alignaligns text and inline things, but doesn't align block elements (e.g. normal divs). -
text-align: centerwill not center when content is too wide. It will align left in that case. See also -
By default
widthandheightdoesn't include padding and border.width: 100%withpadding: 10pxcan still overflow the parent.box-sizing: border-boxmake the width/height include border and padding. Note thatwidthincludes scrollbar regardless ofbox-sizing. -
The
<html>and<body>and viewport are 3 different things.- Making web page height fill viewport requires both
htmlandbodyto beheight: 100%. (Another solution isheight: 100dvh) - Viewport propagation. For background-related styles and
overflow, applying to eitherbodyorhtmlwill all make them apply to viewport. But if bothhtmlandbodyspecifies background,<body>'s background won't propagate to viewport and only cover<body>area. If bothhtmlandbodyhaveoverflow: scrollthen there will be two scrollbars.
- Making web page height fill viewport requires both
-
About override:
- CSS import order matters. The latter-imported ones can override the earlier ones.
- The styles directly written in HTML are inline styles, which can be set by JS. Inline styles can override attributes in
.cssfiles (when both are not!important).!importantattribute in.cssfiles can override non!importantinline style. - Browser puts some user agent styles to
<input>and<button>(e.g.color,font-family). So<input>and<button>will not inherit some styles from parent. - See CSS cascade for complete details.
-
About hiding:
- Parent
visibility: hiddendoesn't enforce all children to be hidden. If child hasvisibility: visibleit will still be shown. This don't apply toopacity: 0ordisplay: none. - An element with
opacity: 0can still be interacted (e.g. click button). This doesn't apply todisplay: noneorvisibility: hidden. display: noneremoves element from layout. This doesn't apply tovisibility: hiddenoropacity: 0.
- Parent
-
The
<!DOCTYPE html>in the beginning of html is important. Without it, browsers will use "quirks mode" which make many behaviors different. See also -
- It's recommended to specify
widthandheightattribute in<img>to avoid layout shift due to image loading delay.
- It's recommended to specify
-
JS-in-HTML may interfere with HTML parsing. For example
<script>console.log('</script>')</script>makes browser treat the first</script>as ending tag. See also -
Virtual scrolling breaks Ctrl-F (Cmd-F) search.
-
Trailing slash in URL. If current URL is
https://xxx.com/aaa/bbb, then<img src="image.png">use imagehttps://xxx.com/aaa/image.png. But if current URL ishttps://xxx.com/aaa/bbb/(with trailing slash), then image path ishttps://xxx.com/aaa/bbb/image.png
Unicode and text
- Two concepts: code point, grapheme cluster:
- Grapheme cluster is the "unit of character" in GUI. An emoji is a grapheme cluster, but it may consist of many code points.
- In UTF-8, a code point can be 1, 2, 3 or 4 bytes. The byte number does not necessarily represent code point number.
- In UTF-16, each UTF-16 code unit is 2 bytes. A code point can be 1 code unit (2 bytes) or 2 code units (4 bytes, surrogate pair 9).
- JSON string
\uescape uses surrogate pair."\uD83D\uDE00"in JSON has only one code point.
- Strings in different languages:
- Rust use UTF-8 for in-memory string.
s.len()gives byte count. Rust does not allow directly indexing on astr(but allows subslicing).s.chars().count()gives code point count. Rust is strict in UTF-8 code point validity. - Java, C# and JS's string encoding is similar to UTF-16 10. String length is code unit count. Indexing works on code units. Each code unit is 2 bytes. One code point can be 1 code unit or 2 code units.
- In Python,
len(s)gives code point count. Indexing gives a string that contains one code point. - C++
std::stringand Golangstringhave no constraint of encoding and are similar to byte arrays. - No language mentioned above do string length and indexing based on grapheme cluster.
- In SQL,
varchar(100)limits 100 code points (not bytes).
- Rust use UTF-8 for in-memory string.
- When reading text data in chunk, don't convert individual chunks to string then concat, as it may cut inside a UTF-8 code point.
- Some Windows text files have byte order mark (BOM) at the beginning. It's U+FEFF zero-width no-break space (it's normally invisible). FE FF means file is in big-endian UTF-16. EF BB BF means UTF-8. Some non-Windows software doesn't handle BOM.
- When converting binary data to string, often the invalid places are replaced by � (U+FFFD).
- Directly putting binary data to string loses information, except in C++ and Golang. Even in C++ and Golang it will still lose information after serializing to JSON (use Base64 for binary data in JSON).
- Confusable characters. Some common examples:
"and“”. Microsoft Word and Google Doc auto-replace former to latter.- – (en dash) and - (minus-hyphen). Google Doc auto-replace -- to en dash.
- ......
- Normalization. For example é can be U+00E9 (one code point) or U+0065 U+0301 (two code points). String comparision works on binary data and don't consider normalization.
- Zero-width characters, Invisible characters
- For example, there are many spaces: Normal space U+0020, no-break space U+00A0, em space U+2003, ......
- Line break. Windows often use CRLF
\r\nfor line break. Linux and macOS often use LF\nfor line break. - Locale (elaborated below).
Floating point
-
NaN. Floating point NaN is not equal to any number including itself. NaN == NaN is always false (even if the bits are same). NaN != NaN is always true. Computing on NaN usually gives NaN (it can "contaminate" computation). NaN corresponds to many different binary values.
-
There are +Inf and -Inf. They are not NaN.
-
There is a negative zero -0.0 which is different to normal zero. The negative zero equals zero when using floating point comparision. Normal zero is treated as "positive zero". The two zeros behave differently in some computations (e.g.
1.0 / 0.0 == Inf,1.0 / -0.0 == -Inf,log(0.0) == -Inf,log(-0.0)is NaN) -
JSON standard doesn't allow NaN or Inf:
- JS
JSON.stringifyturns NaN and Inf to null. - Python
json.dumps(...)will directly writeNaN,Infinityinto result, which is not compliant to JSON standard.json.dumps(..., allow_nan=False)will raiseValueErrorif has NaN or Inf. - Golang
json.Marshalwill give error if has NaN or Inf.
- JS
-
Directly compare equality for floating point may fail due to precision loss. Compare equality by things like
abs(a - b) < 0.00001 -
JS use floating point for all numbers. The max "safe" integer is . Outside of the "safe" range, most integers cannot be accurately represented. For large integer it's recommended to use
BigInt.If a JSON contains an integer larger than that, and JS deserializes it using
JSON.parse, the number in result will be likely inaccurate. The workaround is to use other ways of deserializing JSON or use string for large integer. 11 -
Floating-point is 2-based. It cannot accurately represent most decimals. 0.1+0.2 gets 0.30000000000000004 .12
-
Associativity law and distribution law doesn't strictly hold because of precision loss. See also: Defeating Nondeterminism in LLM Inference, Taming Floating-Point Sums
-
Division is much slower than multiplication (unless using approximation). Dividing many numbers with one number can be optimized by firstly computing reciprocal then multiply by reciprocal.
-
These things can make different hardware have different floating point computation results:
- Hardware FMA (fused multiply-add) support.
fma(a, b, c) = a * b + c(in some placesa + b * c). Most modern hardware make intermediary result in FMA have higher precision. Some old hardware or embedded processors don't do that and treat it as normal multiply and add. - Floating point has a Subnormal range to make very-close-to-zero numbers more accurate. Most mondern hardware can handle them, but some old hardware and embedded processors treat subnormals as zero.
- Rounding mode. The standard allows different rounding modes like round-to-nearest-ties-to-even (RNTE) or round-toward-zero (RTZ).
- In X86 and ARM, rounding mode is thread-local mutable state can be set by special instructions. It's not recommended to touch the rounding mode as it can affect other code.
- In GPU, there is no mutable state for rounding mode. Rasterization often use RNTE rounding mode. In CUDA different rounding modes are associated by different instructions.
- Math functions (e.g. sin, log) may be less accurate in some embedded hardware or old hardware.
- Legacy X86 FPU (80-bit floating point registers and per-core rounding mode state).
- ......
- Hardware FMA (fused multiply-add) support.
-
Floating point precision is low for values with very large absolute value or values very close to zero. It's recommended to avoid temporary result to have very large absolute value or be very close-to-zero.
-
Iteration can cause error accumulation. For example, if something need to rotate 1 degree every frame, don't cache the matrix and multiply 1-degree rotation matrix every frame. Compute angle based on time then re-calculate rotation matrix from angle.
Time
- Leap second. Unix timestamp is "transparent" to leap second. Converting between Unix timestamp and UTC time assumes leap second doesn't exist. It's used with leap smear: make the time "stretch" or "squeeze" near a leap second to "hide" existence of leap second.
- Time zone. UTC and Unix timestamp is globally uniform. But human-readable time is time-zone-dependent. It's recommended to store timestamp in database and convert to human-readable time in UI, instead of storing human-readable time in database.
- Daylight Saving Time (DST): In some regions people adjust clock forward by one hour in warm seasons. When DST ends, 1:00 AM to 2:00 AM 13 will run twice, so converting human-readable time in this range to timestamp is ambiguous. Python has
foldto address this ambiguity. - NTP sync may cause time to "jump backward" or "jump forward".
- It's recommended to configure the server's time zone as UTC. Different nodes having different time zones will cause trouble in distributed system. After changing system time zone, the database may need to be reconfigured or restarted.
- There are two clocks: hardware clock and system clock. The hardware clock itself doesn't care about time zone. Linux treats it as UTC by default. Windows treats it as local time by default.
- Verification of certificate uses time. If time is inaccurate, SSL/TLS may not work.
- The "timestamp" may be in seconds, milliseconds or nanoseconds.
- About
Mandmin date format: in JavaSimpleDateFormat,Mis month,mis minute. But in Pythondatetime,mis month,Mis minute. - In DuckDB, when importing a CSV, it guesses date format based on samples by default. There is ambiguity between
DD-MM-YYYYandMM-DD-YYYY. If all days are below 12 DuckDB may guess wrong. See also - The result of MySQL
timestampvalue and PostgreSQLtimesamp with time zone(timestamptz) depends on session time zone. Session time zone can be changed via SQL (set time_zone = ...in MySQL andset time zone ...in PostgreSQL). When using connection pooling, the effect of changing session time zone may interfere other places. 14 - MySQL
timestampis 32-bit. It cannot represent time after 2038-01-19 03:14:07.
Java
==compares object reference. Should use.equalsto compare object content.- Forget to override
equalsandhashcode. It will use object identity equality by default in map key and set. - Mutate the content of map key object (or set element object) makes the container malfunciton (unless the mutation doesn't affect
equalsandhashcode). - Not all
List<T>are mutable.Collection.emptyList()gives immutable list.Arrays.asList()gives list that cannot add element. - A method that returns
Optional<T>may returnnull. - Null is ambiguous. If
get()on a map returns null, it may be either value is missing or value exists but it's null (can distinguish bycontainsKey). Null field and missing field in JSON are all mapped to null in Java object. See also. Similarily, privimtive value 0 can also be ambiguous. - Implicitly converting
Integertointcan causeNullPointerException, same forFloat,Long, etc. - Return in
finallyblock swallows any exception thrown in thetryorcatchblock. The method will return the value fromfinally. - Interrupt. Some libraries ignore interrupt. If a thread is interrupted and then load a class, and class initialization has IO, then class may fail to load.
- Thread pool does not log exception of tasks sent by
.submit()by default. You can only get exception from the future returned by.submit(). Don't discard the future. AndscheduleAtFixedRatetask silently stop if exception is thrown. - Literal number starting with 0 will be treated as octal number. (
0123is 83) - When debugging, debugger will call
.toString()to local variables. Some class'.toString()has side effect, which cause the code to run differently under debugger. This can be disabled in IDE. - Before Java24 virtual thread can be "pinned" when blocking on
synchronizedlock, which may cause deadlock. It's recommended to upgrade to Java 24 if you use virtual thread. finalize()running too slow blocks GC and cause memory leak. Exceptions out offinalize()are not logged. A dead object can resurrect itself infinalize(). It's recommended to useCleanerrather than overridingfinalize.OmitStackTraceInFastThrowoptimization causes exception to have no stacktrace. See also. The first few exceptions have stacktrace, so the stacktrace may be in early logs.
Golang
append()reuses memory region if capacity allows. Appending to a subslice can overwrite parent if they share memory region.deferexecutes when the function returns, not when the lexical scope exits.defercapture mutable variable.- About
nil:- There are nil slice and empty slice (the two are different). But there is no nil string, only empty string. The nil map can be read like an empty map, but nil map cannot be modified.
- Interface
nilweird behavior. Interface pointer is a fat pointer containing type info and data pointer. If the data pointer is null but type info is not null, then it will not equalnil. - Receiving from or sending to
nilchannel blocks forever.
- Before Go 1.22, loop variable capture issue.
- Different kinds of timeout. The complete guide to Go net/http timeouts
- Having interior pointer to an object keeps the whole object alive. This may cause memory leak.
- Forgetting to cancel context cause
<-ctx.Done()to deadlock. - For
WaitGroup,Addmust be called beforeWait. Don'tAddin a new goroutine (unless with proper synchronization). sync.Mutexshould be passed by pointer not value. Same applies tosync.WaitGroupsync.Condnet.Connetc. But slices, maps and channels can be passed by value.
C/C++
- Don't use
=to compare equality. - Storing a pointer to an element in
std::vectorand then grow the vector, vector may re-allocate content, making element pointer invalid. Similar to other containers. std::stringcreated from literal string may be temporary. Takingc_str()from a temporary string is wrong.- Iterator invalidation. Modifying a container when looping on it.
std::views::filtermalfunctions when element is mutated that predicate result changes in multi-pass iteration. See also.std::views::as_rvaluewithstd::ranges::tomutates the element which can trigger that issue. See alsostd::removedoesn't remove but just rearrange elements.eraseactually removes.- Literal number starting with 0 will be treated as octal number. (
0123is 83) - Destructing a deep tree structure can stack overflow. Solution is to replace recursion with loop in destructor.
std::shared_ptritself is not atomic (although its reference count is atomic). Mutating ashared_ptritself is not thread-safe.std::atomic<std::shared_ptr<...>>is atomic.- For
std::mapandstd::unordered_map,map[key]alone will mutate the map if the corresponding entry doesn't exist. See also - For
std::vector<bool>, result ofoperator[]is a proxy object, notbool&. - Undefined behaviors. The compiler optimization aim to keep defined behavior the same, but can freely change undefined behavior. Relying on undefined behavior can make program break under optimization. See also
- Accessing uninitialized memory is undefined behavior. Converting a
char*to struct pointer can be seen as accessing uninitialized memory, because the object lifetime hasn't started. It's recommended to put the struct elsewhere and usememcpyto initialize it.- Directly trating binary data as struct is undefined behavior, even if the memory is initialized. Because it's treated as object lifetime hasn't started. It also may involve alignment issue. One solution is to put the struct on stack then use
memcpyto initialize it.
- Directly trating binary data as struct is undefined behavior, even if the memory is initialized. Because it's treated as object lifetime hasn't started. It also may involve alignment issue. One solution is to put the struct on stack then use
- Accessing invalid memory (e.g. null pointer) is undefined behavior.
- Integer overflow/underflow is undefined behavior. Note that unsigned integer can underflow below 0. Don't use
x > x + 1to check overflow as it will be optimized tofalse. - Aliasing.
- Strict aliasing rule: If there are two pointers with type
A*andB*, then compiler assumes two pointer can never equal. If they equal, using it to access memory is undefined behavior. Except in two cases: 1.AandBhas subtyping relation 2. converting pointer to byte pointer (char*,unsigned char*orstd::byte*) (the reverse does not apply). 15 - Pointer provenance. Two pointers from two different provenances are treated as never equal. If their address equals, it's undefined behavior. See also
- Strict aliasing rule: If there are two pointers with type
constcan mean both read-only and immutable:- If the original declared object is not
const, you can turn pointer to it asconst T*, in this caseconstmeans read-only 16. You can change the object without triggering undefined behavior. - If the original declared object is
const, then it's deemed immutable. If you useconst_castto turn its pointer toT*then change content, it's undefined behavior. 17 - Use
const volatile T*for read-only pointer to data changable by other threads or outer system.
- If the original declared object is not
- If
bool's binary value is neither 0 or 1, using it is undefined behavior. Similarily if an enum's binary value is not valid, using it is undefined behavior.
- Accessing uninitialized memory is undefined behavior. Converting a
- Alignment.
- For example, 64-bit integer's address need to be disivible by 8. Unaligned memory access is undefined behavior. In ARM, accessing memory in unaligned way can cause crash.
- Alignment can cause padding in struct that waste space.
- Some SIMD instructions only work with aligned data.
- Global variable initialization runs before
main. Static Initialization Order Fiasco. - Start from C++ 11, destructors have
noexceptby default. If exception is thrown out of anoexceptfunction, whole process will crash. - Compiler can auto-generate copy constructor that does shallow copy. It may cause wrong implicit copy then cause double free.
- In signal handler, don't do any IO or locking, don't
printformalloc - Compare signed number with unsigned number. If
ais signed -1,bis unsigned 0, thena > bis true, because it auto-convertsainto unsigned number.
Python
- Default argument is a stored value that will not be re-created on every call.
- Be careful about indentation when copying and pasting Python code.
- In conditons, these things are "falsy": 0,
None, empty string, empty container. Be careful if 0 or empty container represents valid value. Also it can be controlled by implementing__bool__method. - GIL (global interpreter lock) doesn't protect again on-disk data race. Two concurrent threads reading and writing same file may cause data race in file. GIL releases during IO.
zipfile.ZipFiledoesn't do compression ifcompressionargument is not set. (.zipformat can contain files uncompressed.)- Pandas
read_csvwill guess type of each column based on samples, if you don't specifydtype. An outlier can change the type of column. (Similar thing applies to DuckDB)
SQL Databases
- Null is special:
x = nulldoesn't work.x is nullworks. Null does not equal itself, similar to NaN.- Unique index allows duplicating null (except in Microsoft SQL server).
select distincttreat nulls as the same in some databases.count(x)andcount(distinct x)ignore rows wherexis null.
- Date implicit conversion can be timezone-dependent.
- Complex join with disctinct may be slower than nested query. See also
- In MySQL (InnoDB), if string field doesn't have
character set utf8mb4then it will error if you try to insert a text containing 4-byte UTF-8 code point. - MySQL (InnoDB) default to case-insensitive.
- MySQL (InnoDB) can do implicit conversion by default.
select '123abc' + 1;gives 124. - MySQL (InnoDB) gap lock may cause deadlock.
- In MySQL, you can select a field and group by another field. It gives nondeterministic result. (this is disabled start from MySQL 5.7.5, see also)
- Multi-column index
(x, y)cannot be used when only filtering ony. (Except when there are very few differentxvalues, database can do a skip scan that uses the index.) Similarilylike 'abc%'can use index butlike '%abc'cannot. - In SQLite, when table is not
strict, values are dynamically-typed, but it has "type affinity" that does implicit conversion. The typefloating pointhas integer affinity and will auto-convert real number 1.0 to integer 1. The typestringhas numeric affinity and will auto-convert string "01234" to number 1234. It's recommended to always usestricttable. - SQLite by default does not do vacuum. The file size only increases and won't shrink. To make it shrink you need to either manually
vacuum;or enableauto_vacuum. - In SQLite if you don't set
busy_timeout, operations will fail directly if database is locked, without auto retry. - Foreign key implicit locking may cause deadlock.
- When using foreign key, when loading database backup, if the child table is loaded before parent, it will fail to load due to foreign key violation.
- Locking may break repeatable read isolation (it's database-specific).
- Distributed SQL database may doesn't support locking or have weird locking behaviors. It's database-specific.
- If the backend has N+1 query issue, the slowness may won't be shown in slow query log, because the backend does many small queries serially and each individual query is fast.
- Long-running transaction can cause problems (e.g. locking). It's recommended to make all transactions finish quickly.
- If a string column is used in index or primary key, it will have length limit. MySQL applies the limitation when changing table schema. PostgreSQL applies the limitation by erroring when inserting or updating data.
- PostgreSQL
notifyinvolves global locking if used within transaction, see also. Also,listenmalfunctions when used with connection pooling. It also has message size limit. - In PostgreSQL, incrementally updating a large
jsonbis slow, as it internally recreates wholejsonbdata. It's recommended to separate it if you do incremental update. - Storing UUID as string in database wasts performance. It's recommended to use database's built-in UUID type.
- Also, in some places UUID text doesn't have hyphen (e.g.
6cdd4753e57047259dd7024cb27b4c4finstead of6cdd4753-e570-4725-9dd7-024cb27b4c4f). Need to consider it when parsing and comparing UUID.
- Also, in some places UUID text doesn't have hyphen (e.g.
- Whole-table locks that can make the service temporarily unusable:
- In MySQL (InnoDB) 8.0+, adding unique index or foreign key is mostly concurrent (only briefly lock) and won't block operations. But in older versions it may do whole-table lock.
mysqldumpused without--single-transactioncause whole-table read lock.- In PostgreSQL,
create unique indexoralter table ... add foreign keycause whole-table read-lock. To avoid that, usecreate unique index concurrentlyto add unique index. For foreign key, usealter table ... add foreign key ... not valid;thenalter table ... validate constraint .... - In MySQL (InnoDB) an
updateordeletethat cannot use index may lock the whole table, not just targeted rows.
- Querying which range a point is in by
select ... from ranges where p >= start and p <= endis inefficient, even when having composite index of(start, end). 18
Concurrency and Parallelism
volatile:volatileitself cannot replace locks.volatileitself doesn't provide atomicity.- You don't need
volatilefor data protected by lock. Locking can already establish memory order and prevent some wrong optimizations. volatilecan avoid wrong optimization related to reordering and merging memory reads/writes.- In C/C++,
volatiledoesn't establish memory order. But in Java and C#volatileestablishes memory order. 19
- Time-of-check to time-of-use (TOCTOU).
- Data race (it's a large topic, not elaborate here).
- Deadlock and lock-free deadlock.
- MySQL (InnoDB) gap lock may deadlock.
- PostgreSQL write skew. In repeatable read level,
select ... where ... for updatecannot prevent another transaction from inserting new rows that satisfy the query condition. It cannot enforce uniqueness. 20 - Atomic reference counting (
Arc,shared_ptr) can be slow when many threads frequently change the same counter. See also - About read-write lock: trying to write lock when holding read lock will deadlock. The correct way is to firstly release the read lock, then acquire write lock, and the conditions that were checked in read lock need to be re-checked.
- SQL allows a transaction that hold read lock to upgrade to write lock. This mechanism is prone to deadlock.
- Reentrant lock:
- Reentrant means one thread can lock twice (and unlock twice) without deadlocking. Java
synchronizedand C#lockare reentrant. - Non-reentrant means if one thread lock twice, it will deadlock. Rust
Mutexand Golangsync.Mutexare not reentrant.
- Reentrant means one thread can lock twice (and unlock twice) without deadlocking. Java
- False sharing of the same cache line costs performance.
- Try to cancel some async operation, but the callback still runs.
Common in many languages
- Forget to check for null/None/nil.
- When for looping on a container, inserting to or removing from it (iterator invalidation).
- Unintended sharing of mutable data. For example in Python
[[0] * 10] * 10does not create a proper 2D array. - For non-negative integer
(low + high) / 2may overflow. A safer way islow + (high - low) / 2. - Short circuit.
a() || b()will not runb()ifa()returns true.a() && b()will not runb()whena()returns false. - Operator precedence.
a || b && cisa || (b && c). - Assertion should not be used for validating external data. Validating external data should use proper error handling. Assertion should check internal invariants.
- Confusing default value with missing value. For example, if the balence field is primitive integer, 0 can represent both "balance value not initialized" or "balance is really 0".
- The same thing also applies to primitive values in protocolbuffer. To discriminate, field must be marked
optionaland app code must call generatedhas*method to check.
- The same thing also applies to primitive values in protocolbuffer. To discriminate, field must be marked
- When using profiler: the profiler may by default only include CPU time which excludes waiting time. If your app spends 90% time waiting (e.g. wait on database), the flamegraph may not include that 90% which is misleading.
- When getting files in a folder, the order is not deterministic (may depend on inode order). It may behave differently on different machines even with same files. It's recommended to sort by filename then process.
- Note that
lsby default sorts results. Usels -fto see raw file order.
- Note that
- The order in hash map is also non-deterministic (unless using linked hash map).
- IO buffering.
- If you don't flush, it may delay actual write.
- A CLI program that don't flush stdout works fine when directly running in terminal, but it delays output when used with pipe
|.
- A CLI program that don't flush stdout works fine when directly running in terminal, but it delays output when used with pipe
- If program is force-killed (e.g.
kill -9) some of its last log may not be written to log file because it's buffered. - In Linux, if
write()andclose()both don't return error code, the write may still fail, due to IO buffering. See also
- If you don't flush, it may delay actual write.
- Modulo of negative numbers. In Python,
a % bisa - (floor(a / b) * b). But in C/C++/Java/C#/JS/Rust/Golang,a % bisa - (roundTowardZero(a / b) * b). Ifais negative then the behavior will be weird. - Retrying without limit or retrying without timeout leaks resources.
Transitive dependency conflict
Indirectly use different versions of the same package (diamond dependency issue).
- In Java, maven will only pick one version. If there is incompatibility, may result in errors like
NoSuchMethodErrorat runtime.- Shading can make two versions of the same package co-exist by renaming.
- In JS, node.js allows two versions of same package to co-exist. Their
let,constglobal variables and classes will separately co-exist. But other global variables are shared.- If two versions of React are used together, it may give "invalid hook call" error.
- If two versions of a React component library use together, it may have context-related issues.
- Python doesn't allow two versions os same package to co-exist. (Sometimes this creates "dependency hell".)
- In C/C++ it may give "duplicate symbol" error in static linking.
- Rust allows two different major versions of same crate to co-exist. It de-duplicates according to semantic versioning (See also, See also). Their global variables also separately co-exist. Having two major versions of Tokio causes problem.
Linux and bash
- If the current directory is moved,
pwdstill shows the original path.pwd -Pshows the real path. cmd > file 2>&1make both stdout and stderr go to file. Butcmd 2>&1 > fileonly make stdout go to file but don't redirect stderr.- There is a capability system for executables, apart from file permission sytem. Use
getcapto see capability. - Unset variables. If
DIRis unset,rm -rf "$DIR/"becomesrm -rf "/". Usingset -ucan make bash error when encountering unset variable. - Bash has caching between command name and file path of command. If you move one file in
$PATHthen invoking it in command gives ENOENT. Refresh cache usinghash -r - Using a variable unquoted will make spaces separate it into different arguments. Also it will make its line breaks treated as space.
set -ecan make the script exit immediately when a sub-command fails, but it doesn't work inside function whose result is condition-checked (e.g. the left side of||,&&, condition ofif). See alsofork()creates a new process that has only one thread. If another thread holds lock during forking, that lock will never release.fork()also has potential of security issues.- File name can contain
\n\r'". File name can be invalid UTF-8. - In Linux file names are case-sensitive, different to Windows and macOS.
- glibc compatibility issue. A program that's build in a new Linux distribution dynamically links with a new version of glibc, then it may be incompatible with old versions of glibc in old systems. Can be fixed by static linking glibc or using containers 21.
- Path trailing slash:
- If
/aaa/bbbis a symbolic link to a folder,rm /aaa/bbbremoves the symbolic link, butrm /aaa/bbb/may remove files in pointed folder. - For
mv x.txt /aaa/bbb, if/aaa/bbbis a folder it will move file into the folder, but if/aaa/bbbdoesn't exist it will rename file name tobbb.
- If
Backend-related
- K8s
livenessProbeused with debugger. Breakpoint debugger usually block the whole application, making it unable to respond health check request, so it can be killed by K8slivenessProbe. - Don't use
:latestimage. They can change at any time. - In Redis, getting keys by a prefix
KEYS prefix-*is a slow operation that will traverse all keys. Use Redis hash map for that use case. - Kafka's message size limit is 1MB by default.
- In Kafka, across partitions, consume order may be different to produce order. If key is null then message's partition is not deterministic.
- In Kafka, if a consumer processes too slow (no acknowledge within
max.poll.interval.ms, default 5 min), the consumer will be treated as failed, then a rebalance occurs. That timeout is per-batch. If a batch contains too many messages it may reach that timeout even if individual message processing is not slow. Can fix by reducing batch sizemax.poll.records. - If you put your backend behind Nginx, you need to configure connection reuse, otherwise under high concurrency, connection between nginx and backend may fail, due to not having enough internal ports.
- Nginx
proxy_bufferingdelays SSE. - If the backend behind Nginx initiates closing the TCP connection, Nginx passive health check treat it as backend failure and temporarly stop reverse proxying. See also
- Nginx configuration URL trailing slash. See also
- Elasticsearch doesn't allow removing mapping in an index. Dynamic mapping can auto-add mappings that you cannot remove, and it's enabled by default. 22
- Elasticsearch terms aggregation result is inaccurate on large datasets. Increasing
shard_sizecan alleviate but increase resource usage. Composite aggregation is more accurate.
React
- React compares equality using reference equality, not content equality.
- The objects and arrays that are newly created in component rendering 23 are treated as always-new. Use
useMemoto fix 24. - The closure functions that are created in component rendering are also always-new. Use
useCallbackto fix. - If an always-new thing is put into
useEffectdependency array, the effect will run on every component function call. See also Cloudflare indicent 2025 Sept-12. - Don't forget to include dependencies in the dependency array. And the dependencies also need to be memoed.
- The objects and arrays that are newly created in component rendering 23 are treated as always-new. Use
- About state:
- State objects themselves should be immutable. Don't directly set fields of state objects. Always recreate whole object.
- Don't set state directly in component rendering. State can only be set in callbacks.
useEffectwithout dependency array runs on every component render. ButuseEffectwith empty dependency array[]runs only on component mounting.- Forget clean up in
useEffect. - Closure trap. Closure can capture a state. If the state changes, the closure still captures the old state. Solutions:
- Make closure not capture state and access state within
useReducer. - Put mutable thing in
useRef(note that changing value in ref don't trigger component re-rendering,) - Add state to effect dependency array. But if the effect manages
setInterval, doing this will make timing inaccurate.
- Make closure not capture state and access state within
useEffectfirstly runs in next iteration of event loop, after browser renders the web page. Doing initialization inuseEffectis not early enough and may cause visual flicker. UseuseLayoutEffectfor early initialization.
Git
- Rebasing and squashing rewrite history. If local already-pushed history is rewritten, normal push will give conflicts, need to use force push. If remote history is rewritten, normal pull will give conflicts, need to use
--rebasepulling.- Force pushing with
--force-with-leasecan sometimes avoid overwriting other developers' commits. But if you fetch then don't pull,--force-with-leasecannot protect.
- Force pushing with
- Sometimes rebasing requires you to solve the same conflict many times (because multiple commits touch the same conflict line). Squashing changes before rebasing can avoid it.
- After commiting files, adding these files into
.gitignorewon't automatically exclude them from git. To exclude them, delete them.- You can also use
git rm --cachedto exclude them without deleting locally. However, after excluding and pushing, when another coworker pulls, these files will be deleted (not just excluded).
- You can also use
- Reverting a merge doesn't fully cancel the side effect of the merge. If you merge B to A and then revert, merging B to A again has no effect. One solution is to revert the revert of merge.
- A cleaner way to cancel a merge, instead of reverting merge, is to 1. backup the branch, 2. hard reset to commit before merge, 3. cherry pick commits after merge, 4. force push.
- In GitHub, if you accidentally commited secret (e.g. API key) and pushed to public, even if you override it using force push, GitHub will still keep that secret public. See also, Example activity tab
- In GitHub, if there is a private repo A and you forked it as B (also private), then when A becomes public, the private repo B's content is also publicly accessible, even after deleting B. See also.
- GitHub by default allows deleting a release tag, and adding a new tag with same name, pointing to another commit. It's not recommended to do that. It breaks build system caching. It can be disabled in rulesets configuration. For external dependencies, hardcoding release tag may be not enough to prevent supply chain risk.
git stash popdoes not drop the stash if there is a conflict.- In Windows, Git often auto-convert cloned text files to be CRLF line ending. But in WSL many software (e.g. bash) doesn't work with files with CRLF. 25
- macOS auto adds
.DS_Storefiles into every folder. It's recommended to add**/.DS_Storeinto.gitignore. - In Windows and macOS, file name is case-insensitive. Renaming file that only change letter case won't be tracked by git (renaming using
git mvworks normally).
Networking
- Some routers and firewall silently kill idle TCP connections without telling application. Some code (like HTTP client libraries, database clients) keep a pool of TCP connections for reuse, which can be silently invalidated (using these TCP connection will get RST). To solve it, configure system TCP keepalive. See also 26
- The result of
tracerouteis not reliable. See also. Sometimes tcptraceroute is useful. - TCP slow start can increase latency. Can be fixed by disabling
tcp_slow_start_after_idle. See also - TCP sticky packet. Nagle's algorithm delays packet sending. It will increase latency. Can be fixed by enabling
TCP_NODELAY. See also - The HTTP protocol does not explicitly forbit GET and DELETE requests to have body. Some places do use body in GET and DELETE requests. But many libraries and HTTP servers does not support them.
- One IP can host multiple websites, distinguished by domain name. The HTTP header
Hostand SNI in TLS handshake carries domain name, which are important. Some websites cannot be accessed via IP address. - CORS (cross-origin resource sharing). For requests to another website (origin), the browser will prevent JS from getting response, unless the server's response contains header
Access-Control-Allow-Originand it matches client website. This requires configuring the backend. Passing cookie to another website involves more configuration. If your frontend and backend are in the same website then there is no CORS issue. - Reverse path filtering. When routing is asymmetric, packet from A to B use different interface than packets from B to A, then reverse path filtering rejects valid packets.
- In old versions of Linux, if
tcp_tw_recycleis enabled, it aggressively recycles connection based on TCP timestamp. NAT and load balancer can make TCP timestamp not monotonic, so that feature can drop normal connections. - When using SSL/TLS in private network unconnected to internet, the client may try to check certificate revocation status from internet, which will timeout.
- Certificate expire. Examples: Starlink incident, LinkedIn incident, Microsoft Teams incident
- Auto certificate renewal may silently stop working. Example
Locale
- The upper case and lower case can be different in other natural languages. In Turkish (tr-TR) lowercase of
Iisıand upper case ofiisİ. The\w(word char) in regular expression can be locale-dependent. - Letter ordering is different in some other natural languages. Regular expression
[a-z]may malfunction in other locale. - PostgreSQL linguistic sorting (collation) depends on glibc by default. Upgrading glibc may cause index corruption due to changing of linguistic order. See also. Related: Docker Postgres Image issue
- Text notation of floating-point number is locale-dependent.
1,234.56in US correspond to1.234,56in Germany. - CSV normally use
,as spearator. But in Germany locale separator is;. - Han unification. The same code point may appear differently in different locales. Usually a font will contain variants for different locales. Correct localization requires choosing the correct font variant. HTML code
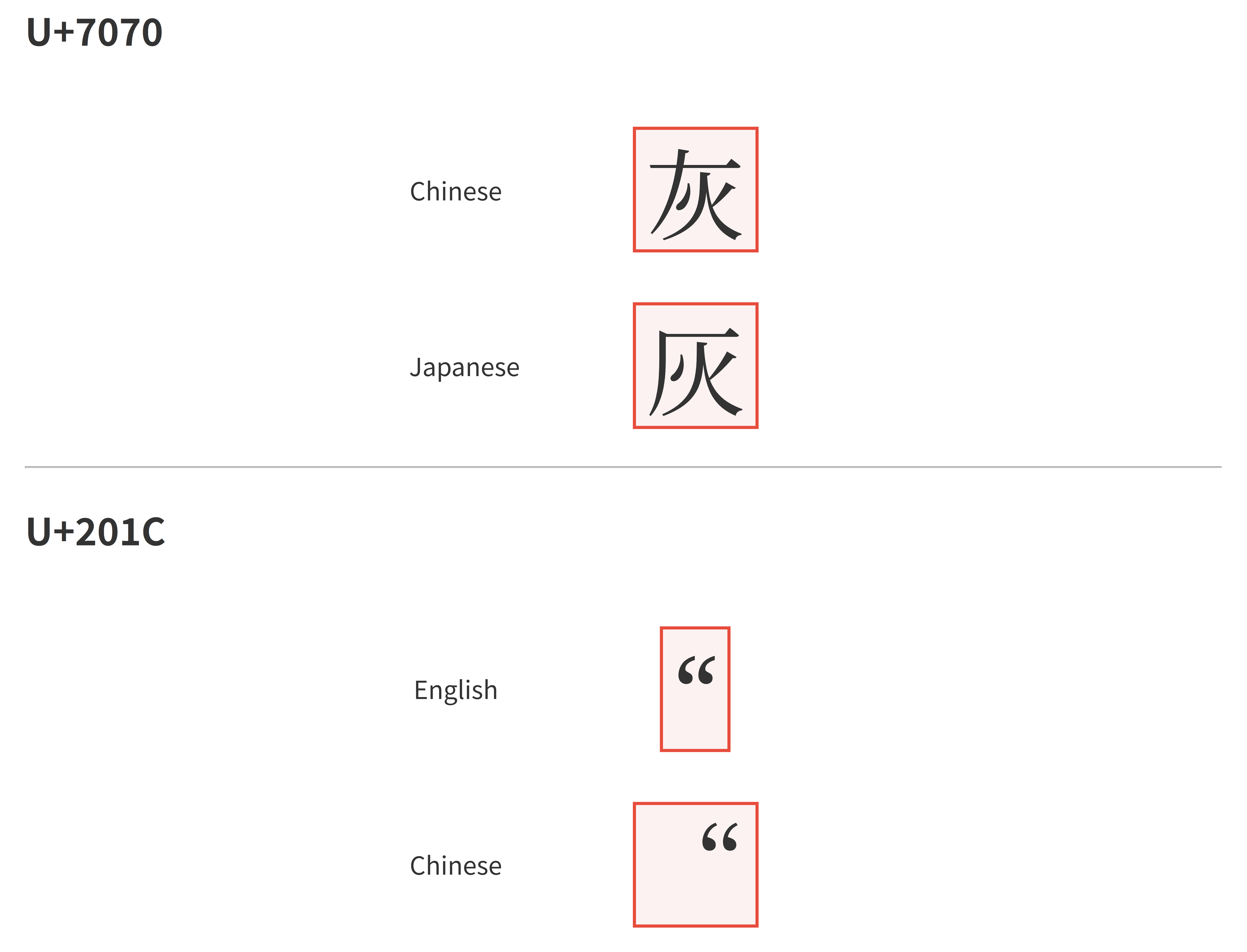
Regular expression
- Regular expression cannot parse the syntax that allows infinite nesting (because it uses finite state machine. Infinite nesting require infinite states). HTML allows infinite nesting. But it's ok to use regex to parse HTML of a specific website.
- Regular expression behavior can be locale-dependent (depending on which regular expression engine).
- There are many different "dialects" of regular expression. Don't assume a regular expression that works in JS can work in Java.
- A separate regular expression validation can be out-of-sync with actual data format. Crowdstrike incident was caused by a wrong separate regular expression validation. It's recommended to avoid separate regular expression validation. Reuse parsing code for validation. See also: Parse, don't validate
- Email validation is not easy. See also
- Backtracking performance issue. See also: Cloudflare indicent 2019 July-2, Stack Exchange incident 2016 July-20
Microsoft-related
- When using Microsoft Excel to open a CSV file, Excel will do a lot of conversions, such as date conversion (e.g. turn
1/2and1-2into2-Jan) and Excel won't show you the original string. The gene SEPT1 was renamed due to this Excel issue. Excel will also make large numbers inaccurate (e.g. turn12345678901234567890into12345678901234500000) and won't show you the original accurate number, because Excel internally use floating point for number. Related: 2010 British intelligence phone number issue. - Windows limits command length to 32767 code units. See also
- In Windows the default stack size of main thread is 1MB, but in Linux and macOS it's often 8MB. It's easier to stack overflow in Windows by default.
- In Windoes, environment variable names are case-insensitive.
- Windows limits path length to be 260 code units by default.
Other
- YAML:
- YAML is space-sensitive, unlike JSON.
key:valueis wrong.key: valueis correct. - YAML doesn't allow using tab for indentation.
- Norway country code
NObecome false if unquoted. - Git commit hash may become number if unquoted.
- Two different extensions of YAML file:
.ymland.yaml. Some places only accept one of them. - See also: The yaml document from hell
- YAML is space-sensitive, unlike JSON.
- It's recommended to configure billing limit when using cloud services, especially serverless. See also: ServerlessHorrors
- Big endian and little endian in binary file and net packet.
- The current working directory can be changed by system call (e.g.
chdir). - The formats
.zipand.mp4are container formats. They can hold many different kinds of formats inside.
Footnotes
-
CSS only try to expand if the available space is finite. In may cases it has infinite vertical space by default. ↩
-
Browser will draw the stacking context into a seprate "image", then draw the image to web page (or parent stacking context). The weirdness of stacking context are caused by this separate drawing mechanism. ↩
-
In macOS it can be configured to make scrollbar take space like in Windows. ↩
-
The CSS box model includes content box, padding, border and margin, but doesn't mention scrollbar. Scrollbar is visually between border and padding. Scrollbar is conceptually in padding box. But if the inner content is not intrinsically-sized, scrollbar occupies space from content box ("steal" space across padding). See also. One may ask "if width includes scrollbar, then why
width: 100vwcause horizontal overflow"? Becausewidth: 100vwapplies to an element inside viewport, not viewport itself. Viewport width includes viewport's scrollbar. ↩ -
It avoids circular dependency where parent height is determined by content height, but content height is determined by parent height. ↩
-
In Nov 2025
calc-sizeis not yet supported by FireFox and Safari. ↩ -
Also, there is another solution for transition
height: auto: transitioningmax-heightfrom 0 to a large value, but I don't recommend it as it will mess up animation timing. ↩ -
When adding a new element, initial transition animation won't work by default. But if you read its layout-related value (e.g.
offsetHeight) between changing animated attribute, it will trigger a reflow and make initial transition work. ↩ -
The U+XXXX notation (XXXX is a hex value) represents a code point. There is some ambiguity of "code point" in UTF-16. In UTF-16, for a code point formed by two code units (4 bytes), its two individual code units are also code points, but these two are surrogate code points. It can be seen as both one code point and two code points, which is confusing. The code points from U+D800 to U+DFFF are called surrogate code points. The code points that are not surrogate are called scalar values. For that code point formed by two code units (4 bytes), it's one scalar value, it's also two surrogate code points. From string semantic value, it should be seen as one code point (scalar value). This ambiguity doesn't exist in UTF-8. In this article, code point refers to scalar value. ↩
-
Strictly speaking, they use WTF-16 encoding, which is similar to UTF-16 but allows invalid surrogate pairs. That encoding is for API and is not necessarily the actual in-memory representation. For example, Java has an optimization that use Latin-1 encoding (1 byte per code point) for in-memory string if possible. ↩
-
Putting millisecond timestamp integer in JSON fine, as millisecond timestamp exceeds limit in year 287396. But nanosecond timestamp suffers from that issue. ↩
-
It's recommended to NOT use floating point to store money value. Note that Microsoft Excel uses floating point to represent number, and many financial data are processed in Excel. Excel has rounding so that 0.30000000000000004 is displayed as 0.3 . Only use Excel for finance if you don't require high precision. Doing rough financial analyzing in Excel is fine. ↩
-
In some regions it's 2:00 AM to 3:00 AM. ↩
-
It's recommended to avoid using these timezone-related types and avoid changing session time zone. Use timezone-independent types (
datetimein MySQL andtimestamp without time zonein PostgreSQL, orbigintin both databases) in UTC in database, then convert to local time in UI. ↩ -
Using pointer type to hold integer is fine as long as you don't use it to access memory. But it's not recommended to do that. ↩
-
The read-only here means in-language constraint. It should not be confused with read-only memory which is actually immutable. ↩
-
In C++, changing
mutablefield of aconstobject is not undefined behavior. See also. ↩ -
It's recommended to use spatial index in MySQL and GiST in PostgreSQL for ranges. For non-overlappable ranges, it's possible to efficiently query using just B-tree index:
select * from (select ... from ranges where start <= p order by start desc limit 1) where end >= p(only require index ofstartcolumn). ↩ -
In Java,
volatileaccesses have sequentially-consistent ordering (JVM will use memory barrier instruction if needed). In C#, writes tovolatilehave release ordering, reads tovolatilehave acquire ordering (CLR will use memory barrier instruction if needed). Note that "release" and "acquire" in memory order is different to locking (but related to locking). ↩ -
It can be solved in serializable level. Without serializable level, it can also be solved by special constraints. For conditional uniqueness constraint, use partial unique index. For range uniqueness constraint, use range type and exclude constraint. For uniqueness across two tables, insert redundant data into another table with unique constraint. (Related: in MySQL repeatable read level,
select ... for updatewill do gap lock on index which can prevent write skew, but gap lock may cause deadlock.) ↩ -
There is a "fix problem then create new problem then fix new problem" cycle in deployment. Firstly dynamic linking creates dependency hell, then solve it using containers. But containers are slow to rebuild, which slows down development iteration cycle. Then tools like tilt solve the problem by "hacking" container (replace binary without rebuilding container). There are other hacks such as putting binary in mounted folder outside of container. But the root problem (dynamic linking dependency hell) can be just fixed by static linking. ↩
-
Removing mapping requires reindexing. Reindexing not only costs performance, but also has risks of losing new data during reindexing, because reindex works on the snapshot. Zero-downtime reindexing that doesn't lose new ingested data during reindexing is hard: 1. create new index 2. new document ingests to both old index and new index (dual-writing) 3. reindex 4. make queries go to new index 5. stop ingesting to old index and delete old index. It can be simple if you can accept a downtime. It can also be simple if you don't care about losing new data during reindexing. Also if you can accept duplicated query result during reindex, you can use an alias that includes both old and new index, then no dual-writing needed. ↩
-
Word "render" has ambiguity. The React component rendering means calling the component function. It doesn't draw contents on web page. It's different to browser rendering, which draws contents on web page. ↩
-
In JS,
stringis primitive type, not object type. In JS you don't need to worry about two strings with same content but different reference like in Java. However theStringin JS is object and use refernce equality. ↩ -
Using
git clone --config core.autocrlf=false -c core.eol=lf ...can make git clone as LF. ↩ -
Note that HTTP/1.0 Keep-Alive is different to TCP keepalive. ↩